Nov 28, 28280
May 15, 15150
Jan 4, 4040
Jan 1, 1010
Identifying and upsampling important frames from demonstration data can significantly boost imitation learning from histories, and scales easily to complex settings such as autonomous driving from vision.
Oct 8, 8080
Aug 1, 1010
Aug 1, 1010
We show empirically that the sample complexity and asymptotic performance of learned non-linear controllers in partially observable settings continues to follow theoretical limits based on the difficulty of state estimation
May 7, 7070
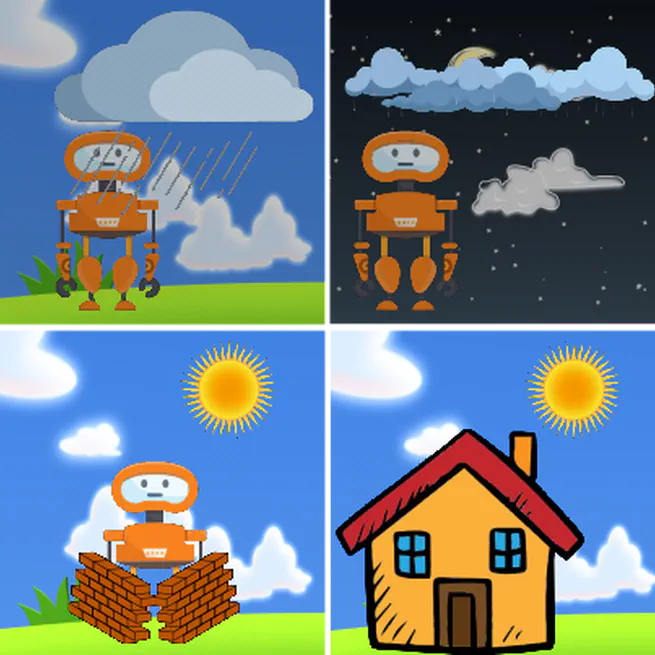
We formulate homeostasis as an intrinsic motivation objective and show interesting emergent behavior from minimizing Bayesian surprise with RL across many environments.
Jan 30, 30300
Jan 1, 1010
We learn reward functions in unsupervised object keypoint space, to allow us to follow third-person demonstrations with model-based RL.
Oct 15, 15150
Oct 15, 15150
To plan towards long-term goals through visual prediction, we propose a model based on two key ideas: (i) predict in a goal-conditioned way to restrict planning only to useful sequences, and (ii) recursively decompose the goal-conditioned prediction task into an increasingly fine series of subgoals.
Jun 1, 1010
How to train RL agents safely? We propose to pretrain a model-based agent in a mix of sandbox environments, then plan pessimistically when finetuning in the target environment.
Jun 1, 1010
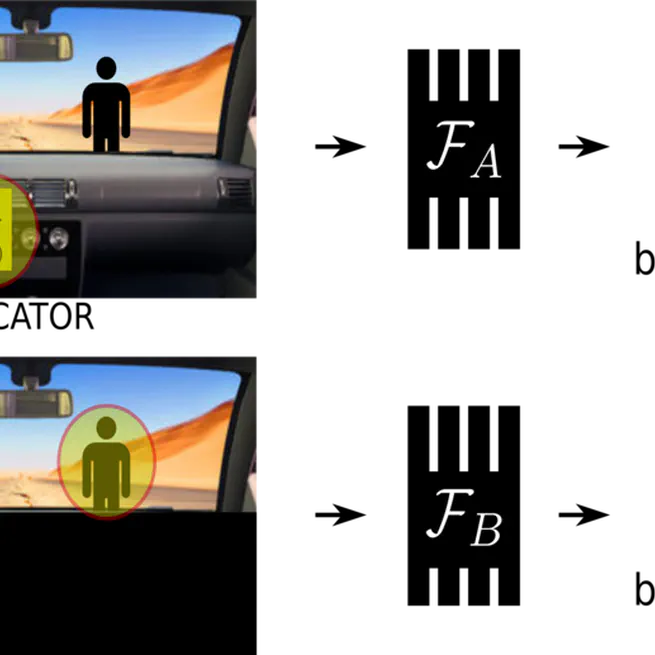
"Causal confusion", where spurious correlates are mistaken to be causes of expert actions, is commonly prevalent in imitation learning, leading to counterintuitive results where additional information can lead to worse task performance. How might one address this?
Dec 12, 12120
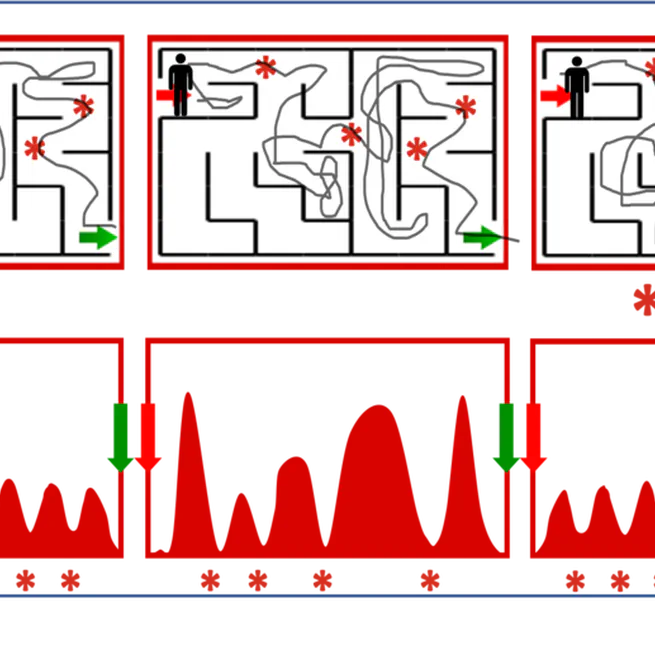
In visual prediction tasks, letting your predictive model choose which times to predict does two things: (i) improves prediction quality, and (ii) leads to semantically coherent "bottleneck state" predictions, which are useful for planning.
Jan 1, 1010
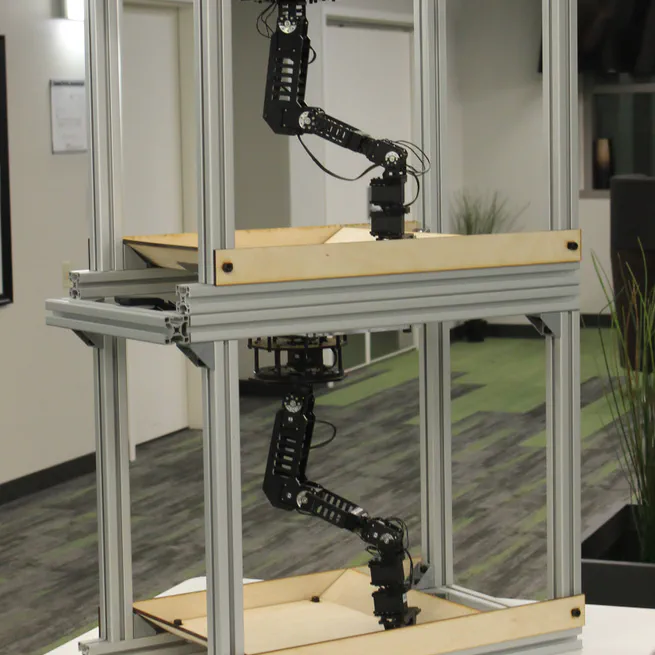

We propose a low-cost compact easily replicable hardware stack for manipulation tasks, that can be assembled within a few hours. We also provide implementations of robot learning algorithms for grasping (supervised learning) and reaching (reinforcement learning). Contributions invited!
Jan 1, 1010
High-resolution tactile sensing together with visual approaches to prediction and planning with deep neural networks enables high-precision tactile servoing tasks.
Jan 1, 1010
Jan 1, 1010
Appearance-based image representations in the form of viewgrids provide a useful framework for learning self-supervised image representations by training a network to reconstruct full object shapes, or scenes.
Jan 1, 1010
Task-agnostic visual exploration policies may be trained through a proxy "observation completion" task that requires an agent to "paint" unobserved views given a small set of observed views.
Jan 1, 1010
Assuming a world that mostly changes smoothly, continuous video streams entail implicit supervision that can be effectively exploited for learning visual representations.
Jan 1, 1010
By exploiting human-uploaded web videos as weak supervision, we may train a system that learns what good videos look like, and tries to automatically direct a virtual camera through precaptured 360-degree videos to try to produce human-like videos.
Jan 1, 1010
Unsupervised feature learning from video benefits from paying attention to changes in appearance of objects detected by an objectness measure, rather than only paying attention to the whole scene.
Jan 1, 1010
Active visual perception with realistic and complex imagery can be formulated as an end-to-end reinforcement learning problem, the solution to which benefits from additionally exploiting the auxiliary task of action-conditioned future prediction.
Jan 1, 1010
An agent's continuous visual observations include information about how the world responds to its actions. This can provide an effective source of self-supervision for learning visual representations.
Jan 1, 1010
Zero-shot recognition systems often rely on visual attribute classifiers, which may be noisy. However, this noise is systematic, and if modeled correctly and used together with our proposed approach, zero-shot learning outcomes can be significantly improved.
Jan 1, 1010
While learning multiple attributes with possibly noisy correlations in the training set, it helps to employ a multi-task learning approach that tries to learn classifiers that rely on different parts of the input feature space.
Jan 1, 1010
Image quality assessment datasets have heretofore focused on specific individual distortions rather than a more natural mix of different degrees of various kinds of distortions. We synthesize a dataset to study this latter setting, and compare various existing algorithms.
Jan 1, 1010