Jan 4, 4040
Aug 1, 1010
We learn reward functions in unsupervised object keypoint space, to allow us to follow third-person demonstrations with model-based RL.
Oct 15, 15150
To plan towards long-term goals through visual prediction, we propose a model based on two key ideas: (i) predict in a goal-conditioned way to restrict planning only to useful sequences, and (ii) recursively decompose the goal-conditioned prediction task into an increasingly fine series of subgoals.
Jun 1, 1010
How to train RL agents safely? We propose to pretrain a model-based agent in a mix of sandbox environments, then plan pessimistically when finetuning in the target environment.
Jun 1, 1010
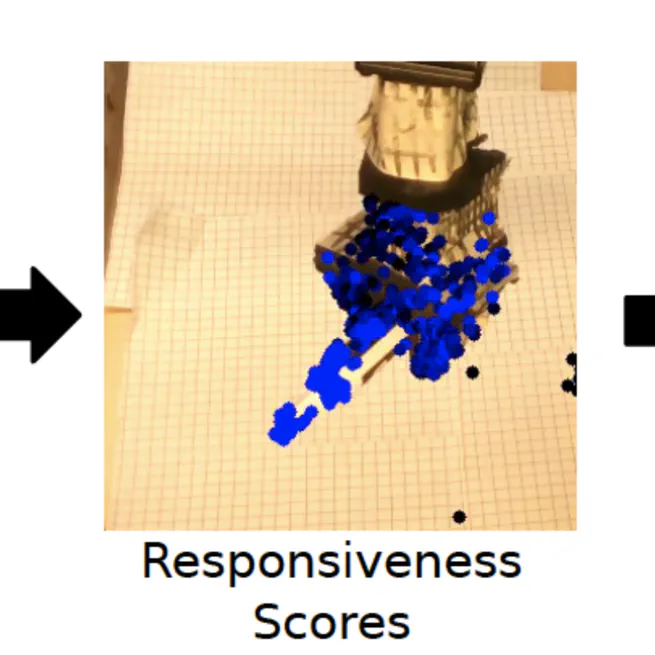
We demonstrate visual control within 20 seconds on a robot with unknown morphology, from a single uncalibrated RGBD camera.
May 17, 17170
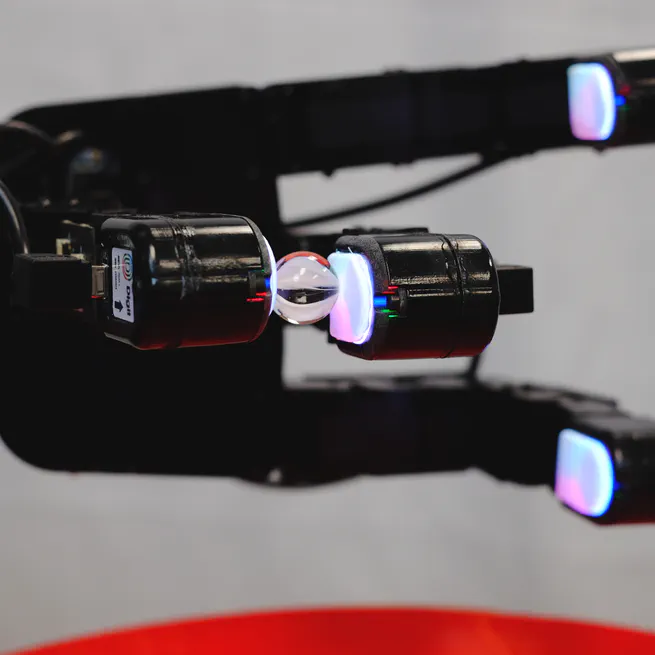
We design and demonstrate a new tactile sensor for in-hand tactile manipulation in a robotic hand.
May 17, 17170
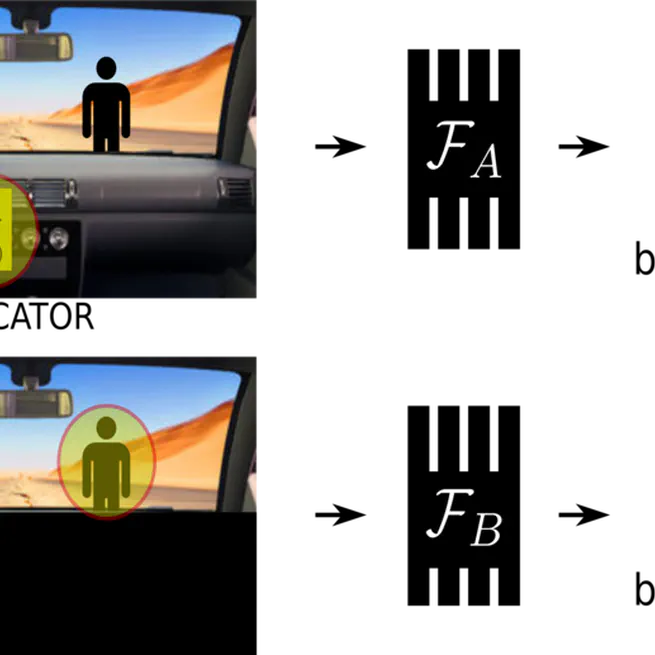
"Causal confusion", where spurious correlates are mistaken to be causes of expert actions, is commonly prevalent in imitation learning, leading to counterintuitive results where additional information can lead to worse task performance. How might one address this?
Dec 12, 12120
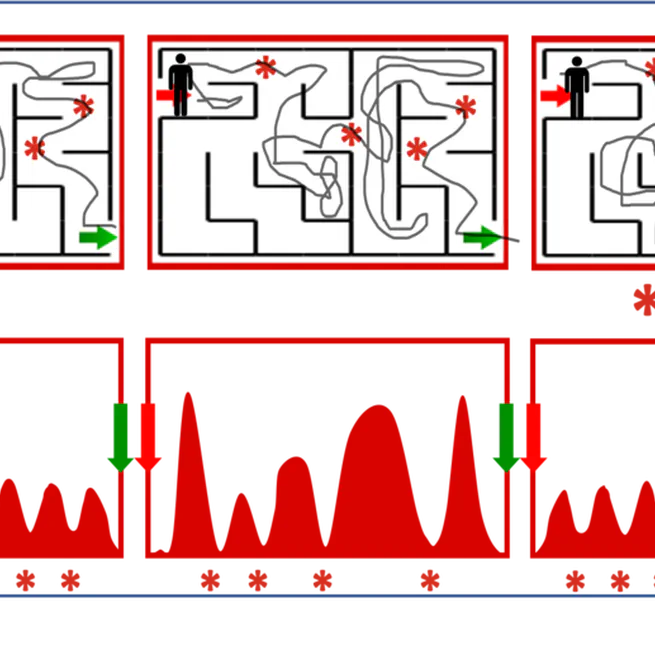
In visual prediction tasks, letting your predictive model choose which times to predict does two things: (i) improves prediction quality, and (ii) leads to semantically coherent "bottleneck state" predictions, which are useful for planning.
Jan 1, 1010
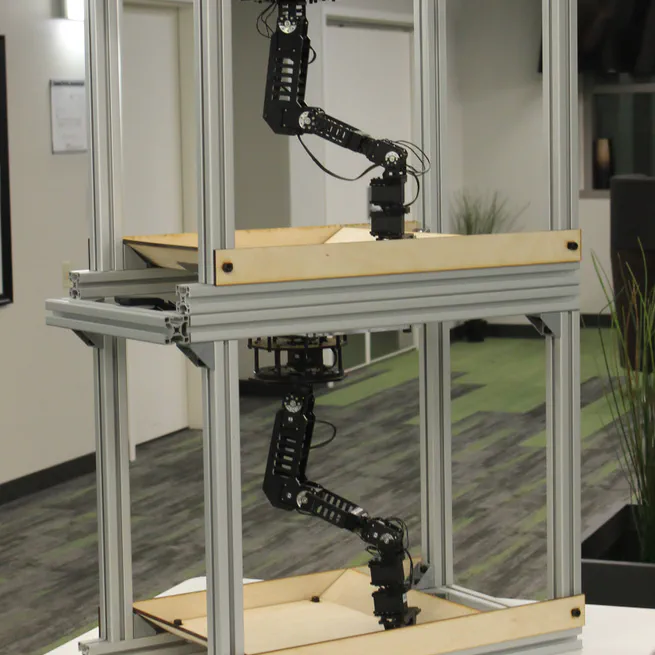

We propose a low-cost compact easily replicable hardware stack for manipulation tasks, that can be assembled within a few hours. We also provide implementations of robot learning algorithms for grasping (supervised learning) and reaching (reinforcement learning). Contributions invited!
Jan 1, 1010
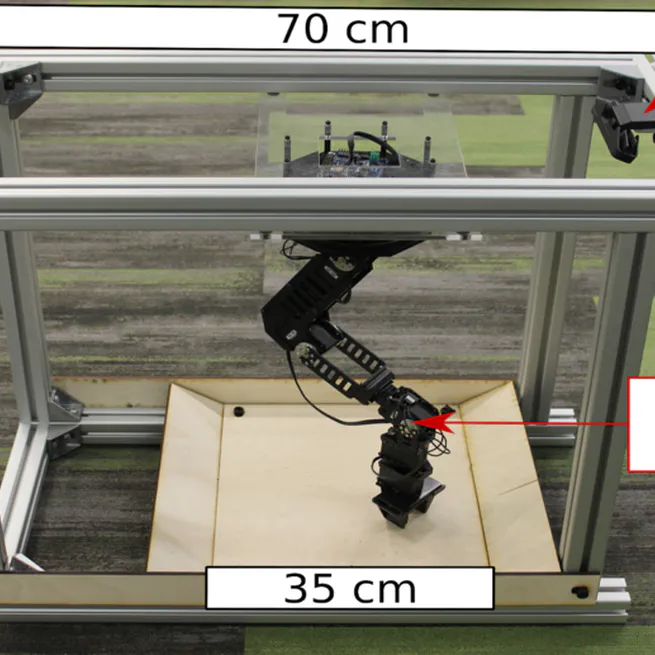
We propose a low-cost compact easily replicable hardware stack for manipulation tasks, that can be assembled within a few hours. We also provide implementations of robot learning algorithms for grasping (supervised learning) and reaching (reinforcement learning). Contributions invited!
Jan 1, 1010
High-resolution tactile sensing together with visual approaches to prediction and planning with deep neural networks enables high-precision tactile servoing tasks.
Jan 1, 1010
By exploiting high precision tactile sensing with deep learning, robots can effectively iteratively adjust their grasp configurations to boost grasping performance from 65% to 94%.
Jan 1, 1010