Remove
- This specifies the overall surface shape(s) to subtract from the data during analysis.
- If the overall shape is not removed, it may dominate the results making it difficult to determine the actual quality of the surface.
- When overall surface shape is subtracted, MetroPro analyzes the difference between a mathematical surface and the actual surface.
- As shown here, removing plane causes this tilted data to be displayed flat, allowing the vertical scale to be expanded, thus revealing much greater detail about the surface.
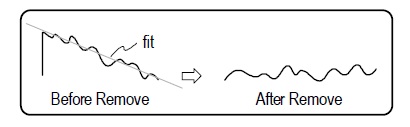
- For the microscopes, the Remove control selects the surface to remove, this usually improves the analysis by eliminating form from the results, thus highlighting the surface irregularities.
- The results are the deviation from the surface you have removed.
- Settings: None, Piston, Plane, Sphere, Cylinder, Fixed Rad Sphere, Fixed Angle Cone, Variable Angle Cone, 4th Order.
- None: when the surface is not continuous, when the surface has an asymmetrical structure such as a large hole or slope, or when you want to see the tilt.
- Piston: compensates for any offset in the z-axis after you null the fringes.
- Plane: compensates for any residual tilt present after you null the fringes. It causes a slanted sample to appear flat. For most analyses, you should remove plane to compensate for the tilt inherent in the equipment setup and the nulling of fringes. Piston is also removed.
- Sphere: causes spherical samples such as ball bearings to appear flat. This allows you to observe surface roughness features instead of the dominant spherical shape. Piston and Plane are also removed.
- Cylinder: causes cylindrical samples such as rods to appear flat. This allows you to observe surface roughness features instead of the dominant cylindrical shape. It can remove two different orthogonal cylinders. Piston and Plane are also removed.
- Fixed Rad Sphere: removes the radius of a sphere whose value is known. The sign convention for a convex surface is a positive radius. A concave surface will have a negative radius. A value must be entered for the Sphere Radius control.
- Fixed Angle Cone: removes a specified cone angle from the data. This value must be entered using the Cone Angle control. An illustration of cone angle is included with the description of the control.
- Var Angle Cone: removes a best fit cone angle from the data. While a cone angle value is not required for this remove routine, entering a valid value in the Cone Angle control can improve processing time.
- 4th Order: removes a best-fit, 4th order polynomial surface.
- Piston, plane, sphere, and cylinder are removed by a least squares fit on the data.
- It calculates the coefficients of the best fit surface and other parameters related to the fit without modifying the data.
- If you have modified the data with an Acquisition mask, only those points remaining are used in the least squares fit.
- Piston and plane are an aspect of the interferometer configuration and the sample, while sphere and cylinder are inherent to the sample.
- Most analyses should be performed with plane removed, while sphere and cylinder should be removed only from samples of certain shapes.
- When sphere or cylinder is selected, piston and plane are also removed.
